What Is Asynchronous Programming?
An asynchronous model allows multiple things to happen at the same time. When your program calls a long-running function, it doesn’t block the execution flow, and your program continues to run. When the function finishes, the program knows and gets access to the result (if there’s a need for that).
Let’s take an example of a program that fetches two files over a network and combines them:
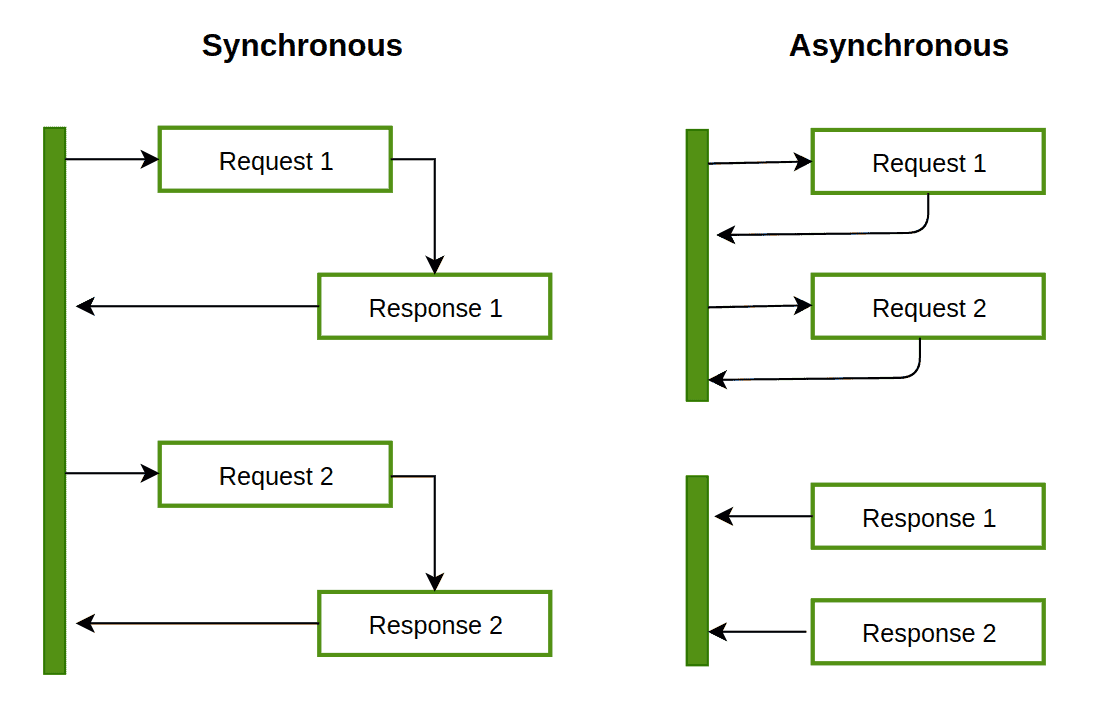
In an asynchronous system, the solution is to start an additional thread of control. The first thread fetches the first file, and the second thread fetches the second file without waiting for the first thread to finish, and then both threads wait for their results to come back, after which they resynchronize to combine their results.
Another example with a single-thread approach is a program that requests a file from the OS and needs to make a mathematical operation.
In an asynchronous system, the program asks the OS for the file and returns the control to the mathematical operation to be executed on the CPU, while waiting for the file.
One approach to asynchronous programming is to make functions that perform a slow action and take an extra argument, a callback function. The action is started, and when it finishes, the callback function is called with the result.